During our wiring on DC fan, there is a optional component mention – Diode. What is this diode use as? Why do we need diode parallel with DC fan. From diode, we will try to understand Bipolar Junction Transistor.

Diode PN Junction
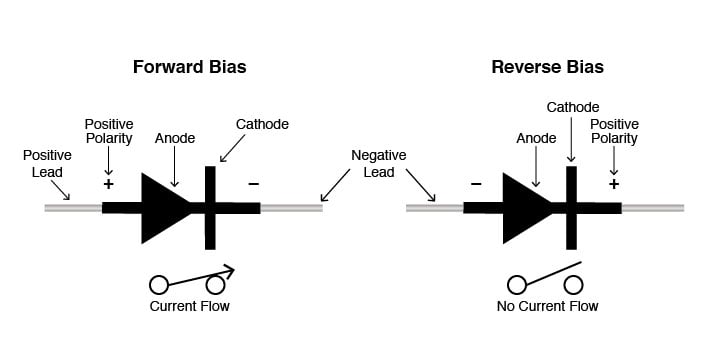
- A diode is a semiconductor device that essentially acts as a one-way switch for current. It allows current to flow easily in one direction.
- Diodes are also known as rectifiers because they change alternating current (ac) into pulsating direct current (dc).
- Diodes have polarity, determined by an anode (positive lead) and cathode (negative lead). Most diodes allow current to flow only when positive voltage is applied to the anode.
- A PN-junction is formed when an N-type material is fused together with a P-type material creating a semiconductor diode.

BJT Transistor
- BJT Transistor is form by joining together two individual signal diodes back-to-back, this will give us two PN-junctions connected together.
- The transistor’s ability to change between these two states enables it to have two basic functions: “switching” (digital electronics) or “amplification” (analogue electronics).
- Bipolar transistors have the ability to operate within three different regions:
- Active Region – the transistor operates as an amplifier
- Saturation – the transistor is “Fully-ON” operating as a switch
- Cut-off – the transistor is “Fully-OFF” operating as a switch

- BJTs are much more suitable than MOSFETs for driving low-power LEDs and similar devices from MCUs.
- MOSFETs are better for high-power applications because they can switch faster than BJTs, enabling them to use smaller inductors in switch-mode supplies, which increases efficiency.
- Intel, one of the largest chip makers in the world, uses practically only FET transistors to build its chips which power billions of devices in the world.
- BJTs are current-controlled. They require a biasing current to the base terminal for operation. Whereas, MOSFETs are voltage-controlled. They only require voltage applied to the gate to turn the MOSFET either on or off. They do not require a biasing current for operation.
Thanks for reading and stay home and stay safe.
[…] our previous article on Diode N BJT Transistor, it had introduced the basic PN diode as one-way switch for current. However, there are more diode […]
LikeLike